被老师要求做PPT给同学讲解一下程序4-7和实验三,只好再认真看下程序并重写了一次实验。重写时,就发现不少问题了。因为这些UNIX的实验网上有代码,所以抄袭借鉴的情况很严重(其实我研一写得也是借鉴的...),但网上能搜到的那几个代码,实在不敢恭维... 小错误不少,加上老师没给test,所以错了估计也发现不了,最典型的如第一个功能,要求是长度不大于4096字节,网上的程序好几个都是 statptr->st_size < 4096,应该是 statptr->st_size <= 4096 呐...
如果你搜到了我写的这个版本,那么恭喜你,你这个实验可以做的很完善。这篇文章可以让你更好的理解这个实验,而且我的代码经仔细修改,保证不坑你~
实验要求
编写程序myfind,命令语法:
myfind <pathname> [-comp <filename> | -name <str>…]
命令语义:
myfind <pathname>的功能:除了具有与程序4-7相同的功能外,还要输出在目录子树之下,文件长度不大于4096字节的常规文件,在所有允许访问的普通文件中所占的百分比。程序不允许打印出任何路径名。 myfind <pathname> -comp <filename>的功能:是常规文件的路径名(非目录名,但是其路径可以包含目录)。命令仅仅输出在 目录子树之下,所有与 文件内容一致的文件的绝对路径名。不允许输出任何其它的路径名,包括不可访问的路径名。 myfind <pathname> -name <str>…的功能:…是一个以空格分隔的文件名序列(不带路径)。命令输出在 目录子树之下,所有与 …序列中文件名相同的文件的绝对路径名。不允许输出不可访问的或无关的路径名。
<pathname> 和 <filename> 均既可以是绝对路径名,也可以是相对路径名。<pathname> 即可以是目录,也可以是文件,此时,目录为当前工作目录。
程序4-7讲解
实验在 《UNIX环境高级编程》程序4-7 -- 递归降序遍历目录层次结构 的基础上完成,所以理解程序4-7是关键。
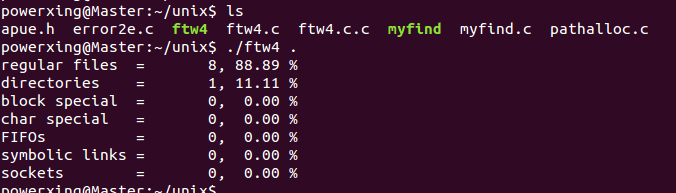
程序4-7的编译:
gcc ftw4.c error2e.c pathalloc.c -o ftw4
运行效果如下图所示:
接着主要说一下理解这个程序所需的几个知识点。
Static 静态全局变量
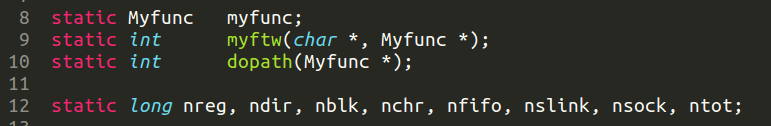
静态变量有不少用处,这边主要体现了两个作用:
- 保证变量初始化。保证 long 正确初始化为 0,可以看到用于统计的 nreg 等变量在程序里是没有显式赋值为 0 的。不同环境下,声明但未赋初值的 int 全局变量不能保证初始化为 0 ,但通过静态声明可以保证。
- 保证变量不冲突。static 声明的全局变量、函数,作用域被限定在该文件内。当多个文件一起编译时,如本程序,各个文件的全局变量、函数是可以互相访问的,通过将只用于本文件的函数和变量声明为静态的,可避免多文件编译时的命名冲突。
通过 typedef 定义函数类型
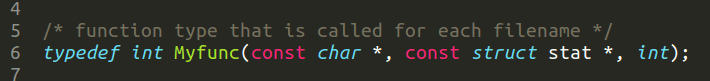
要理解这个定义,首先要了解函数指针的概念。
例如我写了这么一个程序,main()函数里调用say(),由say()调用hi():
#include <stdio.h>
int hi(int x) {
print("hi: %d\n", x);
}
void say(int x) {
hi(x);
}
void main(void) {
say(10);
}
如果我相似实现:在main()里控制say()中调用的函数。即 say(hi, 10);,也就是要传递函数。那通过函数指针就可以做到:
void say(int (*func)(int), int x) {
func(x);
}
void main(void) {
say(hi, 10);
}
使用typedef可以使得程序函数指针的定义更为简洁:
typedef int Myfunc(int);
void say(Myfunc* func, int x) {
func(x);
}
所以再返回来看看程序4-7中的typedef定义,其实就是这样:
typedef int Myfunc(const char *, const struct stat *, int);
static Myfunc myfunc;
// static Myfunc myfunc; 等价于如下的声明:
// static int myfunc(const char *pathname, const struct stat *statptr, int type);
在程序中,myfunc()作为参数,在函数间传递、调用。如 main() 中:
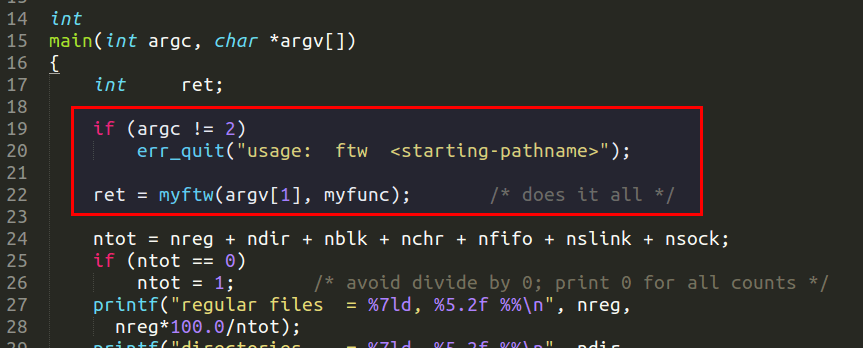
申请空间存储路径
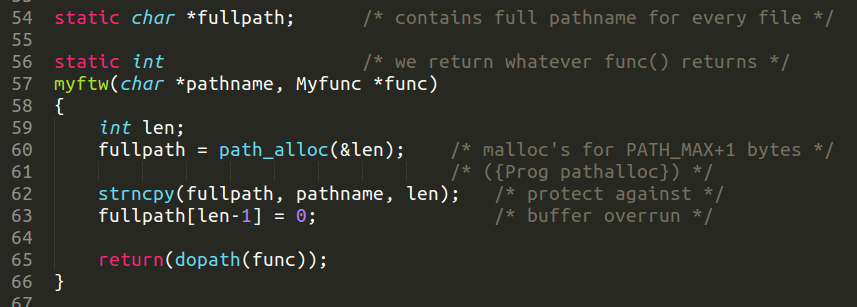
使用了书中程序2-3来分配存储路径的空间,自己直接用 malloc 来分配是不规范的。另外注意使用了 strncpy() 来进行再次处理,确保不会溢出。
dopath(): 递归遍历目录
在 dopath() 中,对每个文件都执行一次 myfunc()。如果是目录的话,首先对目录执行一次 myfunc(),再对目录中每个文件执行一次 myfunc()。
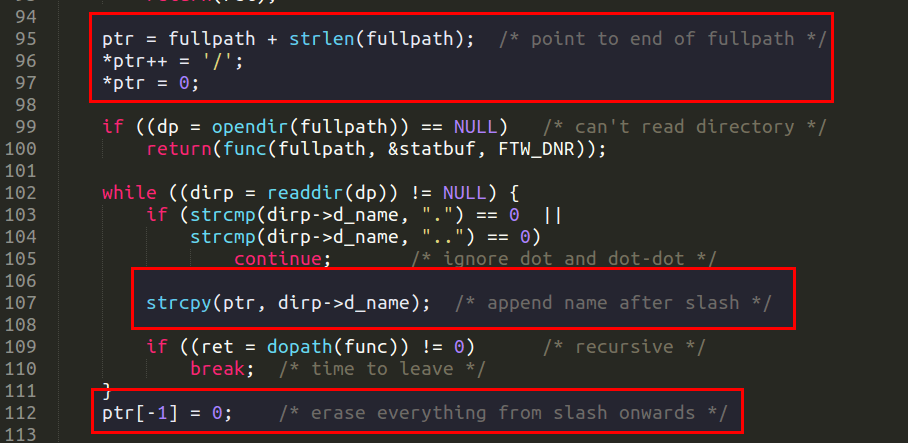
在遍历目录文件时,通过将文件名附加到当前目录之后,就得到了文件路径。strcpy(ptr, dirp->d_name) 是将 dirp->d_name 加到 ptr 开始的地址之后,而进行 *ptr++='/' 的处理是保证当前目录以 '/' 结尾。
这样 strcpy() 拼接路径时,才不会出错,如 fullpath='.'时。
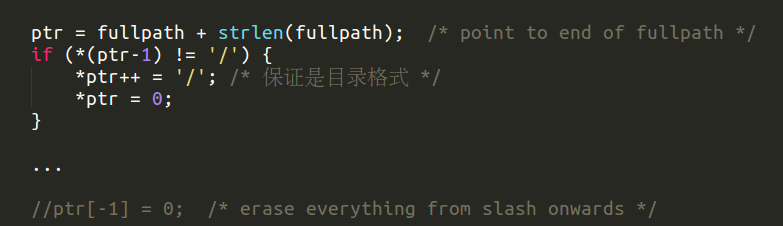
不过目录结果加 '/' 的处理考虑得不够周到,应该先进行判断,判断是否以 '/' 结尾,否则结果中会出现两个 '//' 的路径,虽然这不会影响程序正确性( /home//user/ 跟/home/user/ 一样)。另外切记要去掉之后的 ptr[-1] = 0;
myfunc()
这个函数就是统计各类型文件所占比例。再次记得,通过 dopath(),每个文件和目录都会执行一次myfunc()。
实验的实现
因为目录的遍历已经写好,无需修改(除了处理 '/' 那)。程序4-7的框架具备通用性,我们只需要修改 main() 和 myfunc() 来实现所需功能即可。
如我们可以定义三个函数来实现所需功能(我这边保留了myfunc()):
static Myfunc myfunc, myfuncExtra, myfuncCompareContent, myfuncCompareName;
功能1 统计比例
这个功能比较简单,只要在原来的基础上加个对 文件长度不大于4096字节的普通文件 的判断就行了。
功能2 文件内容一致
思路:对于普通文件,首先比较文件大小,文件大小相同再进行内容的比较。这样可以有效避免无用的打开、读入文件的操作。
要比较内容,首先需要读入,比较的话用 strcmp() 即可:
filebuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*filesize);
fd = open(...);
read(fd, filebuf, filesize);
...
strcmp(filebuf, filebuf2); // 比较内容
功能3 文件名一致
这个功能要解决的一个核心问题是:如何从路径中提取出文件名,比如从 fullpath = './unix/ftw4.c' 提取出 ftw4.c。一个简单的做法就是从末尾向前查找,直到找到第一个 '/',则这个位置之后的内容就是文件名了,再进行比较即可。
获取绝对路径
利用 chdir() 和 getcwd() 可以获取到绝对路径:
chdir("/home/user/");
getcwd(...); -> "/home/user/""
chdir("../");
getcwd(...); -> '/home/'
chdir("/home/user/ftw4.c");
// 出错,需是目录的路径,这边就要想办法只提取出目录
需要注意2点:
- 使用 chdir() 后,当前工作目录就改变了,此时就得注意相对路径了;
- chdir() 参数需是目录,不能是文件路径。
trick
对于要求输出绝对路径的功能,可首先将用户输入的 <pathname> (可能是相对路径)转化为绝对路径,再执行 myfunc,也就是:
int main(argc, argv) {
...
path = absolutepath(argv[1]); // 自己实现 absolutepath 函数
ret = myftw(path, myfunc);
...
}
你可以先按照自己的想法去做这个实验,等你做到某一步,或者你开始考虑一些路径的问题时,你就会明白这个 trick 的作用了。
PS: 这一步可以放在 myftw() 里完成。
实验讲解PPT
把PPT放出来好了(已转成PDF): UNIX实验三讲解PPT下载
完整代码
完整代码如下:
#include "apue.h"
#include <dirent.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
/* function type that is called for each filename */
typedef int Myfunc(const char *, const struct stat *, int);
static Myfunc myfuncExtra, myfuncCompareContent, myfuncCompareName;
static int myftw(char *, Myfunc *);
static int dopath(Myfunc *);
static long n4096, nreg, ndir, nblk, nchr, nfifo, nslink, nsock, ntot;
/* 用于 myfuncCompareContent() 和 myfuncCompareName() */
static long filesize, filefindcount;
static char *filebuf, *comparebuf, *inputpath, *inputfilepath, *inputfilename;
static char *getRealDir(const char *, char *); /* 获取目录的绝对路径 */
static int getFileNamePos(const char *); /* 获得路径中,文件名开始的位置 */
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
struct stat statbuf;
if (!(argc == 2 || (argc == 4 && strcmp(argv[2], "-comp") == 0) || (argc >= 4 && strcmp(argv[2], "-name") == 0)))
err_quit("usage: myfind <pathname> [-comp <filename> | -name <str>…]");
/* <pathname>既可以是目录,也可以是文件,此时,目录为当前工作目录 */
if (lstat(argv[1], &statbuf) < 0) {
err_quit("lstat error: %s\n", argv[1]);
}
if (S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode) == 0) /* not a directory */
strcpy(argv[1], ".");
if (argc == 2) {
ret = myftw(argv[1], myfuncExtra); /* does it all */
ntot = nreg + ndir + nblk + nchr + nfifo + nslink + nsock;
if (ntot == 0)
ntot = 1; /* avoid divide by 0; print 0 for all counts */
printf("regular files = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nreg,
nreg*100.0/ntot);
if (nreg == 0)
nreg = 1; /* nreg 也可能为 0, 后面不会再用到nreg,可以更改 */
printf("(less than 4096 = %7ld, %5.2f %%)\n", n4096,
n4096*100.0/nreg);
printf("directories = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", ndir,
ndir*100.0/ntot);
printf("block special = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nblk,
nblk*100.0/ntot);
printf("char special = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nchr,
nchr*100.0/ntot);
printf("FIFOs = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nfifo,
nfifo*100.0/ntot);
printf("symbolic links = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nslink,
nslink*100.0/ntot);
printf("sockets = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nsock,
nsock*100.0/ntot);
}
/* 找出所有与指定文件有 相同内容 的文件 */
if ( argc == 4 && strcmp(argv[2], "-comp") == 0 ) {
/* 输入判断 */
if (lstat(argv[3], &statbuf) < 0)
err_quit("lstat error: %s\n", argv[3]);
if (!S_ISREG(statbuf.st_mode))
err_quit("that is not a regular file: %s\n", argv[3]);
/* 读入文件内容 */
int fd;
filesize = statbuf.st_size;
if ((fd = open(argv[3], O_RDONLY, FILE_MODE)) == -1)
err_sys("can't open the file '%s'\n", argv[3]);
if ((filebuf = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * filesize)) == NULL ||
(comparebuf = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * filesize)) == NULL)
err_sys("malloc error\n");
if (read(fd, filebuf, filesize) != filesize) {
err_sys("read error '%s'\n", argv[3]);
}
close(fd);
/* 将起始目录转化为绝对路径 */
/* 这样后续的遍历路径就都是绝对路径了 */
int len;
inputpath = path_alloc(&len);
getRealDir(argv[1], inputpath);
/* 额外的完善实现:在搜索结果中过滤掉作为比较的文件 */
/* 既然是作为比较的文件,自身相等这是肯定的,就不该出现在结果中 */
/* 个人理解,觉得不必要可自行删掉 inputfilepath 相关部分 */
/* 首先记录 指定文件 的绝对路径,方便后边进行过滤 */
char *inputfiledir;
inputfiledir = path_alloc(&len);
int pos;
pos = getFileNamePos(argv[3]);
if (pos == 0) { /* 没有路径信息,表明是当前路径 */
strcpy(inputfiledir, ".");
} else {
strncpy(inputfiledir, argv[3], pos);
}
inputfilepath = path_alloc(&len);
getRealDir(inputfiledir, inputfilepath);
/* 先获取 指定文件 所在目录的绝对路径,再加上 文件名 构成文件的绝对路径 */
strcat(inputfilepath, argv[3]+pos); /* argv[3]+pos 是文件名的起始处 */
/* 开始查找 */
printf("\nSame content as '%s':\n", argv[3]);
ret = myftw(inputpath, myfuncCompareContent);
if (filefindcount == 0) printf("Can't find any match file.\n");
printf("\n");
}
/* 找出 指定文件名 的所有文件 */
if ( argc >= 4 && strcmp(argv[2], "-name") == 0 ) {
/* 将搜索目录转化为绝对路径,简化实现 */
int len, i;
int pos;
inputpath = path_alloc(&len);
inputfilename = path_alloc(&len);
getRealDir(argv[1], inputpath);
printf("\n");
for (i = 3; i < argc; i++) { /* 注意输入的文件名可以有多个 */
pos = getFileNamePos(argv[i]);
if (pos != 0) /* 包含路径 */
err_quit("only file name: %s", argv[i]);
strncpy(inputfilename, argv[i], len);
filefindcount = 0;
printf("%d. Same name as '%s':\n", i-2, argv[i]);
ret = myftw(inputpath, myfuncCompareName);
if (filefindcount == 0) printf("Can't find any match file.\n");
printf("\n");
}
}
exit(ret);
}
/*
* Descend through the hierarchy, starting at "pathname".
* The caller's func() is called for every file.
*/
#define FTW_F 1 /* file other than directory */
#define FTW_D 2 /* directory */
#define FTW_DNR 3 /* directory that can't be read */
#define FTW_NS 4 /* file that we can't stat */
static char *fullpath; /* contains full pathname for every file */
static int /* we return whatever func() returns */
myftw(char *pathname, Myfunc *func)
{
int len;
fullpath = path_alloc(&len); /* malloc's for PATH_MAX+1 bytes */
/* ({Prog pathalloc}) */
strncpy(fullpath, pathname, len); /* protect against */
fullpath[len-1] = 0; /* buffer overrun */
return(dopath(func));
}
/*
* Descend through the hierarchy, starting at "fullpath".
* If "fullpath" is anything other than a directory, we lstat() it,
* call func(), and return. For a directory, we call ourself
* recursively for each name in the directory.
*/
static int /* we return whatever func() returns */
dopath(Myfunc* func)
{
struct stat statbuf;
struct dirent *dirp;
DIR *dp;
int ret;
char *ptr;
if (lstat(fullpath, &statbuf) < 0) /* stat error */
return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_NS));
if (S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode) == 0) /* not a directory */
return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_F));
/*
* It's a directory. First call func() for the directory,
* then process each filename in the directory.
*/
if ((ret = func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_D)) != 0)
return(ret);
ptr = fullpath + strlen(fullpath); /* point to end of fullpath */
if (*(ptr-1) != '/') { /* 只有当末尾不是 '/' 时,才需要加,否则会出现 '//' */
*ptr++ = '/'; /* 保证是目录的路径以 '/' 结尾 */
*ptr = 0;
}
if ((dp = opendir(fullpath)) == NULL) /* can't read directory */
return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_DNR));
while ((dirp = readdir(dp)) != NULL) {
if (strcmp(dirp->d_name, ".") == 0 ||
strcmp(dirp->d_name, "..") == 0)
continue; /* ignore dot and dot-dot */
strcpy(ptr, dirp->d_name); /* append name after slash */
if ((ret = dopath(func)) != 0) /* recursive */
break; /* time to leave */
}
//ptr[-1] = 0; /* erase everything from slash onwards */
if (closedir(dp) < 0)
err_ret("can't close directory %s", fullpath);
return(ret);
}
/* 获取绝对路径,且保证目录的绝对路径以斜杠结尾 */
static char*
getRealDir(const char *pathname, char *realpath) {
int len;
char *dirpath, *ptr;
dirpath = path_alloc(&len); /* 记录原来的目录 */
if (getcwd(dirpath, len) == NULL)
err_sys("getcwd fail\n");
if (chdir(pathname) < 0)
err_sys("can't chdir: %s\n", pathname);
if (getcwd(realpath, len) == NULL) /* 记录指定目录的绝对路径 */
err_sys("getcwd fail\n");
ptr = realpath + strlen(realpath);
if (*(ptr-1) != '/') { /* 保证目录的绝对路径以斜杠结尾 */
*ptr++ = '/';
*ptr = 0;
}
if (chdir(dirpath) < 0) /* 还原状态,回到原来的目录 */
err_sys("can't chdir: %s\n", pathname);
return realpath;
}
/* 分离目录和文件名,返回 文件名开始 的位置,在此之前为目录,之后为文件名 */
/* 即返回最后一个 '/' (有可能没有) 的下一位置,即为文件名开始的位置 */
static int
getFileNamePos(const char *pathname) {
int i, pos = 0;
for (i = strlen(pathname)-1; i >= 0; i-- ) {
if (pathname[i] == '/') {
pos = i;
break;
}
}
/* 有可能不包含 '/' */
return (pos == 0) ? pos : pos + 1;
}
/* 遍历目录,并记录文件长度 不大于4096字节 的常规文件的百分比 */
static int
myfuncExtra(const char *pathname, const struct stat *statptr, int type)
{
switch (type) {
case FTW_F:
switch (statptr->st_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFREG:
nreg++;
if (statptr->st_size <= 4096) n4096++;
break;
case S_IFBLK: nblk++; break;
case S_IFCHR: nchr++; break;
case S_IFIFO: nfifo++; break;
case S_IFLNK: nslink++; break;
case S_IFSOCK: nsock++; break;
/* 题目要求不输出无关路径,所以下面的提示信息都可以删掉,我选择注释掉 */
case S_IFDIR: ; /* 如果注释,注意这边得有一个分号 */
// err_dump("for S_IFDIR for %s", pathname);
/* directories should have type = FTW_D */
}
break;
case FTW_D:
ndir++;
break;
case FTW_DNR:
// err_ret("can't read directory %s", pathname);
break;
case FTW_NS:
// err_ret("stat error for %s", pathname);
break;
default: ;
// err_dump("unknown type %d for pathname %s", type, pathname);
}
return(0);
}
/* 找出所有与指定文件有 相同内容 的文件 */
static int
myfuncCompareContent(const char *pathname, const struct stat *statptr, int type) {
/* 只有类型和大小都符合的普通文件,才进行内容是否相同的判断 */
if (type == FTW_F && (statptr->st_mode & S_IFMT) == S_IFREG && statptr->st_size == filesize) {
int fd;
if ((fd = open(pathname, O_RDONLY, FILE_MODE)) == -1)
// err_ret("Can't open file: %s\n", pathname);
return (0); /* 不输出异常文件,直接返回 */
if (read(fd, comparebuf, filesize) != filesize)
err_sys("read error '%s'\n", pathname);
close(fd);
if (strcmp(filebuf, comparebuf) == 0) {
/* 过滤掉作为比较的文件,这步可有可无 */
if (strcmp(inputfilepath, pathname) != 0) {
filefindcount++;
printf("%s\n", pathname);
}
}
}
return (0);
}
/* 找出 指定文件名 的所有文件 */
static int
myfuncCompareName(const char *pathname, const struct stat *statptr, int type) {
if (type == FTW_F) {
int pos;
pos = getFileNamePos(pathname);
if (strcmp(inputfilename, pathname+pos) == 0) {
filefindcount++;
printf("%s\n", pathname);
}
}
return (0);
}