【版权声明】版权所有,严禁转载,严禁用于商业用途,侵权必究。
作者:厦门大学信息学院2021级研究生 费翔
基于Scala语言的Spark数据处理分析案例
案例制作:厦门大学数据库实验室
指导老师:厦门大学信息学院计算机系数据库实验室 林子雨 博士/副教授 E-mail: ziyulin@xmu.edu.cn
相关教材:林子雨,赖永炫,陶继平《Spark编程基础(Scala版)》(访问教材官网)
【查看基于Scala语言的Spark数据分析案例集锦】
一、实验环境
Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
Hadoop 3.1.3
Spark 3.2.0
Scala 2.12.15
Python 3.6.9
此外,使用了Python3相关库进行数据分析与可视化操作,并将实验结果保存为notebook格式以方便后续查看。具体使用的库包括:
- NumPy:Python3语言的扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数据处理操作,并能够方便、高效地对数据进行运算
- Pandas:Python3语言用于数据分析的拓展程序库,提供高性能、易于使用的数据结构和数据分析工具。
- Matplotlib:在Python3绘图领域最为广泛使用的套件,能够方便地实现数据的可视化,并支持用户自定义配置文件与多种输出格式。
- Seaborn:基于Matplotlib进行高级封装对可视化库,能够绘制更加集成化、具有更高风格自由度的图表。
- Jupyter notebook:基于网页的帮助实现交互计算的应用程序,能够使用交互式的笔记本文件格式,实现将代码、文字与数据输出结果进行结合,从而实现一站式的数据处理与分析流程。
- SciPy:开源的Python算法库与数学工具包,包含了基于NumPy的科学计算库。
二、数据预处理
数据集清洗
本项目使用的数据集来自数据网站Kaggle的Covid-19新型冠状肺炎病毒传播数据集,可以直接从百度网盘下载(提取码:ziyu),该数据集包括共67字段,但其中不少字段可以由其它字段数据计算得到,例如“每百万人病例数量 = 1,000,000 * 总病例数 / 国家总人口数”,因此对数据字段进行选择。
字段名称 含义
Continent 所在洲
Location 国家/地区名
Date 数据日期
Total_cases 总病例数
New_cases 当日新增病例数
Total_deaths 总死亡数
New_deaths 当日新增死亡数
Total_vaccinations 接种疫苗总剂次
GDP_per_capita 人均GDP
Population 总人口数
Population_density 人口密度
Median_age 年龄中位数
Life_expectancy 期望寿命
Human_dev_index 人类发展指数
同时,由于数据量较大,但其中很多字段都包含大量空值,因此对数据分析时也需要进行进一步的处理。原数据集中共67字段,但其中大部分字段均缺失了超过六成的数据。对这部分字段数据进行分析时,需要做进一步的判断,删除无效数据。剔除可以通过计算得到的等效字段后,最终选定如上表所示的字段用于分析。数据转换为DataFrame
随后,将数据转换为便于使用的DataFrame格式,以便于后续使用Spark进行分析。首先,启动hadoop伪分布式运行,并将处理好的csv文件存储到HDFS中:
cd /usr/local/hadoop ./sbin/start-dfs.sh bin/hadoop fs -mkdir -p /dbcovid/data bin/hadoop fs -put ~/Downloads/covid.csv /dbcovid/data此时,将csv文件保存至HDFS对应的目录下。可以通过Spark-shell进行检查,通过对路径使用hdfs.exists()方法,确认文件是否存在。随后,需要将保存的数据转换为DataFrame类型。借助课程提供的Spark版本,可以十分容易地直接完成读取:
var datapath = "hdfs://localhost:9000/dbcovid/data/covid.csv" var df = spark.read.option("header", "true").option("inferSchema", "true").csv(datapath)由于考虑到csv文件包含了字段名,因此需要设置header属性为True,否则默认将第一行也会读取为记录值。而对inferSchema属性默认设置的False值,会将所有输入值均作为字符串类型进行保存,因此可以设置为True值以帮助保留浮点数的数据类型。值得注意的是,得益于Spark的处理性能,即使虚拟机仅设置了2GB内存,依然能够在一秒钟内完成创建。此时,可以通过df.printSchema()方法检查得到的数据。

三、使用Spark进行数据分析
在完成数据保存为DataFrame后,可以使用Spark对其进行数据分析。本章首先介绍数据的整体结构,然后对独立字段进行分析,最后对不同字段之间的相关性进行分析。考虑到后续可视化分析需要,此处将语句执行结果获取的数据保存为json文件,使用Spark提供的DataFrame.write.json()方法可以轻松实现。
为了便于使用Spark SQL,需要从DataFrame类型的数据上,建立临时视图:df.createOrReplaceTempView("data")使用Spark SQL可以便于完成后续的操作,具体使用的分析语句见后文。对数据集进行分析得到,该数据集共有166k行记录,其中每一行对应某一个国家在特定日期的疫情情况。数据共包含六大洲、225个国家,以及不属于上述划分的部分数据如全球总数、各大洲总数。对于每一个国家而言,数据记录了最多达774天的病例情况,包括新增/总阳性病例数量,新增/总死亡数量。对于部分国家还包含了总疫苗接种剂次的记录。此外,也包含了国家的基本情况,例如人均GDP、人口、人口密度、年龄中位数、期望寿命与人类发展指数。通过这些数据及其相互联系,可以获得一个国家疫情的传播情况,并与其国家各项指标进行综合分析。
获得上述部分统计指标数值的代码如下:spark.sql("select DISTINCT continent from data") -- 统计洲数量 spark.sql("select COUNT(DISTINCT location) from data") -- 统计国家数量 spark.sql("select COUNT(date) from data where location=='China'").show() -- 统计日期总数独立指标分析
因此,首先定义字符串数组,并在后续的实验中使用循环遍历数组中的国家/地区即可。
var locs = List("China", "United States", "European Union", "Russia", "Japan", "United Kingdom", "Singapore") - (重点国家)新增病例/死亡数量
for (loc <- locs){ spark.sql("select new_cases from data where location='"+loc+"'").write.json("/dbcovid/result/new_cases/"+loc+"/") spark.sql("select new_deaths from data where location='"+loc+"'").write.json("/dbcovid/result/new_deaths/"+loc+"/") } - (重点国家)累计病例/死亡数量
for (loc <- locs){ spark.sql("select total_cases from data where location='"+loc+"'").write.json("/dbcovid/result/total_cases/"+loc+"/") spark.sql("select total_deaths from data where location='"+loc+"'").write.json("/dbcovid/result/total_deaths/"+loc+"/") } - (重点国家)疫苗接种剂次
for (loc <- locs){ spark.sql("select total_vaccinations from data where location='"+loc+"'").write.json("/dbcovid/result/total_vacc/"+loc+"/") } - (全部国家)每百万人累计病例/死亡数量
spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_cases/population) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_cases/") spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_deaths/population) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_deaths/")相关性分析
- (重点国家)每日新增病例数与疫苗接种剂次的关系
for (loc <- locs){ spark.sql("select new_cases,total_vaccinations from data where location='"+loc+"'").write.json("/dbcovid/result/cases_with_vaccs/"+loc+"/") } - (所有国家)每百万人病例/死亡数量与人均GDP的关系
spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_cases/population),max(gdp_per_capita) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_cases_with_gdp/") spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_deaths/population),max(gdp_per_capita) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_deaths_with_gdp/") - (所有国家)每百万人病例/死亡数量与年龄中位数的关系
spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_cases/population),max(median_age) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_cases_with_age/") spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_deaths/population),max(median_age) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_deaths_with_age/") - (所有国家)每百万人病例/死亡数量与人口密度的关系
spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_cases/population),max(population_density) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_cases_with_density/") spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_deaths/population),max(population_density) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_deaths_with_density/") - (所有国家)每百万人病例/死亡数量与期望寿命的关系
spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_cases/population),max(life_expectancy) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_cases_with_lifeexp/") spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_deaths/population),max(life_expectancy) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_deaths_with_lifeexp/") - (所有国家)每百万人病例/死亡数量与人类发展指数的关系
spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_cases/population),max(human_development_index) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_cases_with_hdi/") spark.sql("select location,max(1000000*total_deaths/population),max(human_development_index) from data where continent is not null group by location").write.json("/dbcovid/result/million_deaths_with_hdi/")数据检查与导出
将相应的数据从HDFS导出到系统文件
bin/hdfs dfs -get /dbcovid/result ~/covid_data/四、可视化分析
独立指标分析
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns import json from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter1d # 定义重点国家/地区 locs = ["China", "United States", "European Union", "Russia", "Japan", "United Kingdom", "Singapore"] # 重点国家新增病例数量 path_root = "result/new_cases/"
数据导入
all_data = []
for loc in locs:
path = path_root + loc + ".json"
tmp = pd.read_json(path, lines=True).values.squeeze() # turn to NumPy type
all_data.append(tmp)
all_data = np.array(
[
list(i) + [float("nan")] * (max([len(j) for j in all_data]) - len(i))
for i in all_data
]
)
数据 NaN 值处理
for tmp in all_data:
if np.isnan(tmp[0]):
tmp[0] = 0
for i in range(len(tmp) - 1):
if np.isnan(tmp[i + 1]):
tmp[i + 1] = tmp[i]
数据平滑
for i in range(len(all_data)):
all_data[i] = gaussian_filter1d(all_data[i], sigma=2.5)
保存为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data).transpose()
df.columns = locs
绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Number of new cases')
sns.lineplot(data=df, dashes=False)
plt.show()
重点国家新增死亡数量
path_root = "result/new_deaths/"
all_data = []
for loc in locs:
path = path_root + loc + ".json"
tmp = pd.read_json(path, lines=True).values.squeeze() # turn to NumPy type
all_data.append(tmp)
all_data = np.array(
[
list(i) + [float("nan")] * (max([len(j) for j in all_data]) - len(i))
for i in all_data
]
)
for tmp in all_data:
if np.isnan(tmp[0]):
tmp[0] = 0
for i in range(len(tmp) - 1):
if np.isnan(tmp[i + 1]):
tmp[i + 1] = tmp[i]
for i in range(len(all_data)):
all_data[i] = gaussian_filter1d(all_data[i], sigma=2.5)
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data).transpose()
df.columns = locs
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Number of new deaths')
sns.lineplot(data=df, dashes=False)
plt.show()
重点国家累计病例数量
path_root = "result/total_cases/"
数据导入
all_data = []
for loc in locs:
path = path_root + loc + ".json"
tmp = pd.read_json(path, lines=True).values.squeeze() # NumPy type
all_data.append(tmp)
all_data = np.array(
[
list(i) + [float("nan")] * (max([len(j) for j in all_data]) - len(i))
for i in all_data
]
)
数据 NaN 值处理
for tmp in all_data:
if np.isnan(tmp[0]):
tmp[0] = 0
for i in range(len(tmp) - 1):
if np.isnan(tmp[i + 1]):
tmp[i + 1] = tmp[i]
本数据不使用平滑。
保存为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data).transpose()
df.columns = locs
绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Number of all cases')
sns.lineplot(data=df, dashes=False)
plt.show()
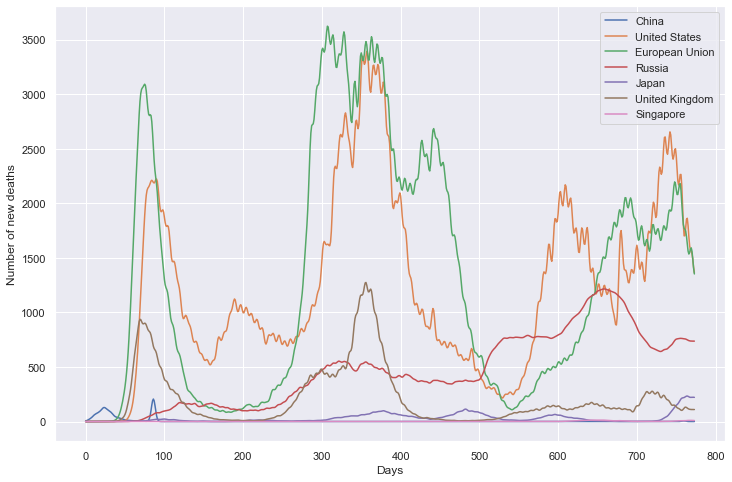
重点国家累计死亡数量
path_root = "result/total_deaths/"
数据导入
all_data = []
for loc in locs:
path = path_root + loc + ".json"
tmp = pd.read_json(path, lines=True).values.squeeze() # NumPy type
all_data.append(tmp)
all_data = np.array(
[
list(i) + [float("nan")] * (max([len(j) for j in all_data]) - len(i))
for i in all_data
]
)
数据 NaN 值处理
for tmp in all_data:
if np.isnan(tmp[0]):
tmp[0] = 0
for i in range(len(tmp) - 1):
if np.isnan(tmp[i + 1]):
tmp[i + 1] = tmp[i]
本数据不使用平滑。
保存为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data).transpose()
df.columns = locs
绘图
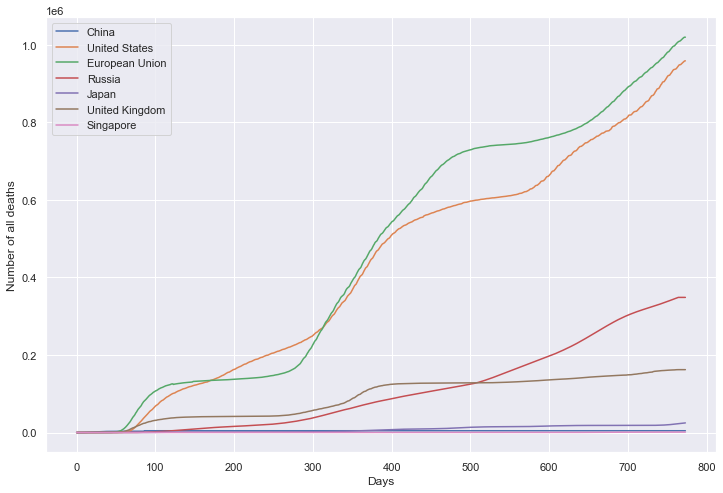
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Number of all deaths')
sns.lineplot(data=df, dashes=False)
plt.show()
重点国家累计疫苗接种剂次
path_root = "result/total_vacc/"
数据导入
all_data = []
for loc in locs:
path = path_root + loc + ".json"
tmp = pd.read_json(path, lines=True).values.squeeze() # NumPy type
all_data.append(tmp)
all_data = np.array(
[
list(i) + [float("nan")] * (max([len(j) for j in all_data]) - len(i))
for i in all_data
]
)
数据 NaN 值处理
for tmp in all_data:
if np.isnan(tmp[0]):
tmp[0] = 0
for i in range(len(tmp) - 1):
if np.isnan(tmp[i + 1]):
tmp[i + 1] = tmp[i]
本数据不使用平滑。
保存为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(all_data).transpose()
df.columns = locs
绘图
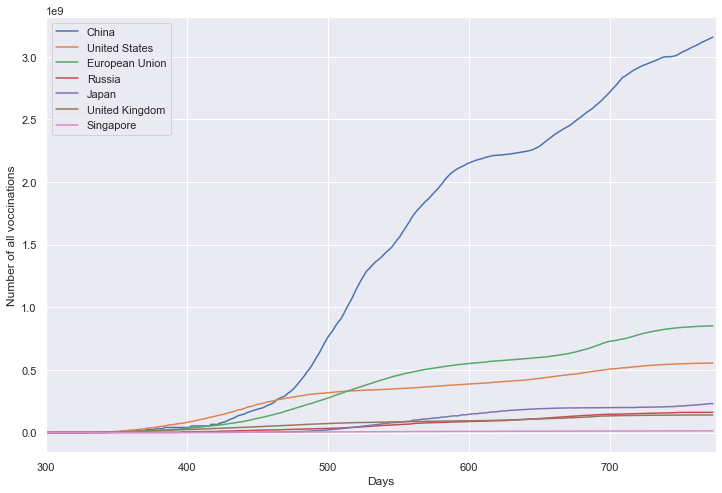
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Number of all voccinations')
fig = sns.lineplot(data=df, dashes=False)
fig.set_xlim(300, 775)
plt.show()
全部国家每百万人累计病例
读取文件
path = "result/million_cases.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data']
tmp_data = pd.DataFrame(all_data, columns=['data']).values.squeeze() # NumPy type
处理 NaN 缺失值
number_data = [x for x in tmp_data if not np.isnan(x)]
保存密度数据
countdata = [0 for in range(15)]
for i in number_data:
count_data[int(i/5e4)] += 1
保存为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(count_data).transpose()
绘图
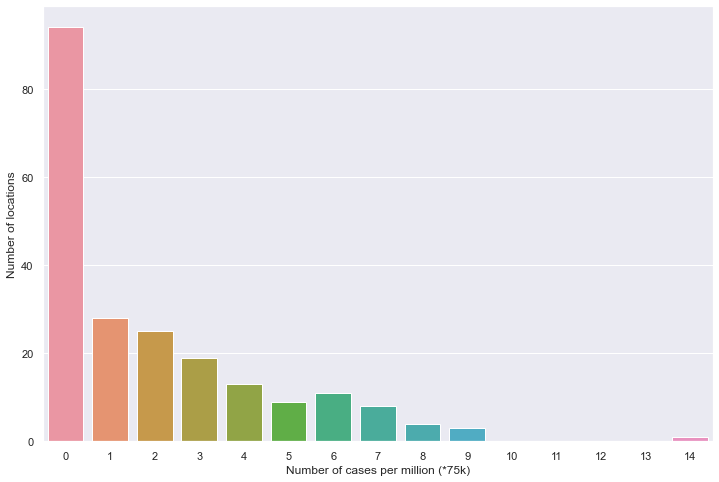
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.barplot(data=df)
plt.xlabel('Number of cases per million (*75k)')
plt.ylabel('Number of locations')
plt.show()
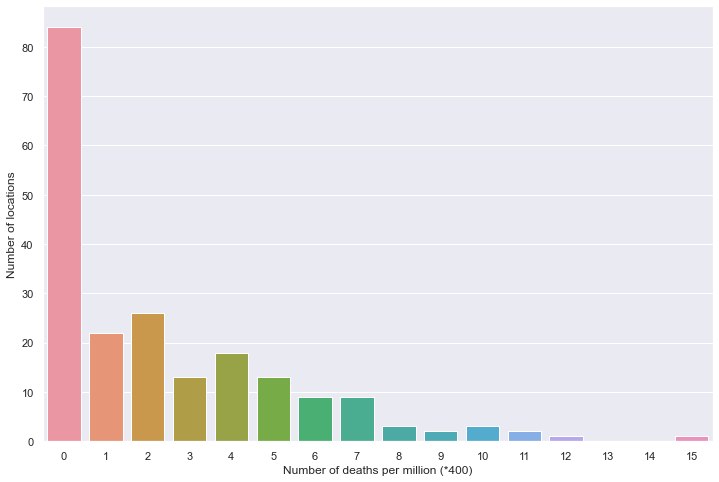
全部国家每百万人累计死亡
读取文件
path = "result/million_deaths.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data']
tmp_data = pd.DataFrame(all_data, columns=['data']).values.squeeze() # NumPy type
处理 NaN 缺失值
number_data = [x for x in tmp_data if not np.isnan(x)]
保存密度数据
countdata = [0 for in range(16)]
for i in number_data:
count_data[int(i/400)] += 1
保存为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(count_data).transpose()
绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.barplot(data=df)
plt.xlabel('Number of deaths per million (*400)')
plt.ylabel('Number of locations')
plt.show()
新增病例数量
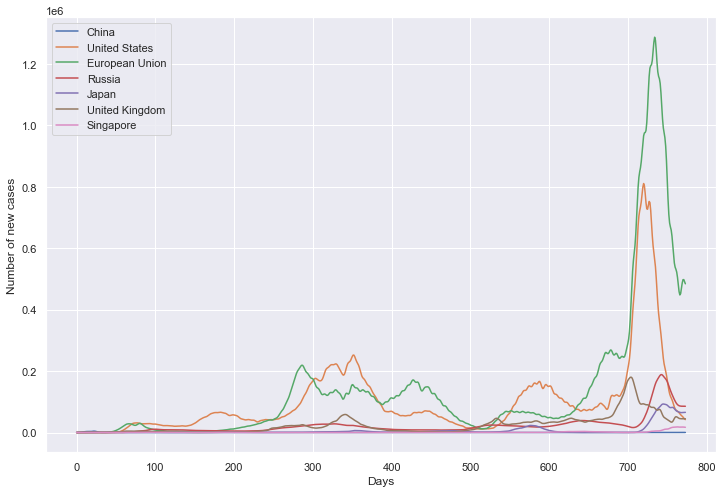
新增死亡数量
累计病例数量
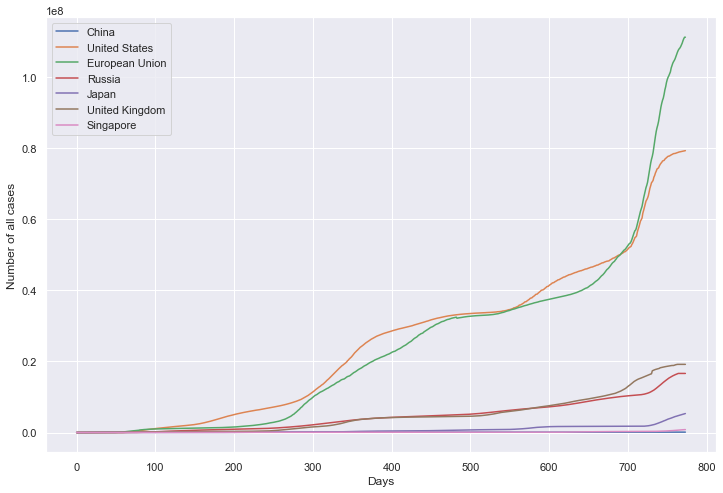
累计死亡数量
累计疫苗数量
百万人累计病例
百万人累计死亡
### 相关性分析
```python
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import json
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter1d
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
# 定义重点国家/地区
locs = ["China", "United States", "European Union", "Russia", "Japan", "United Kingdom", "Singapore"]
# 重点国家新增病例数量与疫苗剂次关系
path_root = "result/cases_with_vaccs/"
# 各国家独立保存图像
for loc in locs:
path = path_root + loc + ".json"
data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True).values.squeeze() # turn to NumPy type
data = np.array(data).T
# 数据 NaN 值处理
for tmp in data:
if np.isnan(tmp[0]):
tmp[0] = 0
for i in range(len(tmp) - 1):
if np.isnan(tmp[i + 1]):
tmp[i + 1] = tmp[i]
# 数据平滑
data[0] = gaussian_filter1d(data[0], sigma=2.5)
# 保存 DataFrame
df0 = pd.DataFrame(data[0])
df0.columns = ['Number of daily new cases']
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data[1])
df1.columns = ['Number of total vaccinations']
# 绘图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.title(loc)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
df0.plot(ax=ax1, style='-')
plt.xlabel('Day')
ax1.set_ylabel('Number of daily new cases')
# ax1.set_yticks(np.arange(0, 1.5e6, 1e5))
plt.legend(loc=2) # 10
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
df1.plot(ax=ax2, style='-', color='green')
ax2.set_ylabel('Number of total vaccinations')
# ax2.set_yticks(np.arange(0, 3.5e9, 5e8))
plt.legend(loc=1) # 10
plt.savefig(u'新增与疫苗关系_'+loc+'.png', bbox_inches='tight')
# 全部国家每百万人累计病例&人均GDP关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_cases_with_gdp.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'gdp']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='gdp', y='data')
plt.xlabel('GDP_per_capita')
plt.ylabel('Number of cases per million')
plt.show()
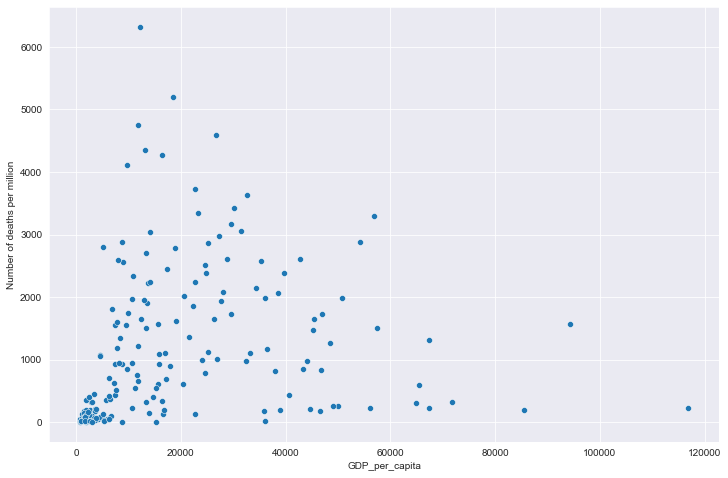
# 全部国家每百万人累计死亡&人均GDP关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_deaths_with_gdp.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'gdp']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='gdp', y='data')
plt.xlabel('GDP_per_capita')
plt.ylabel('Number of deaths per million')
plt.show()
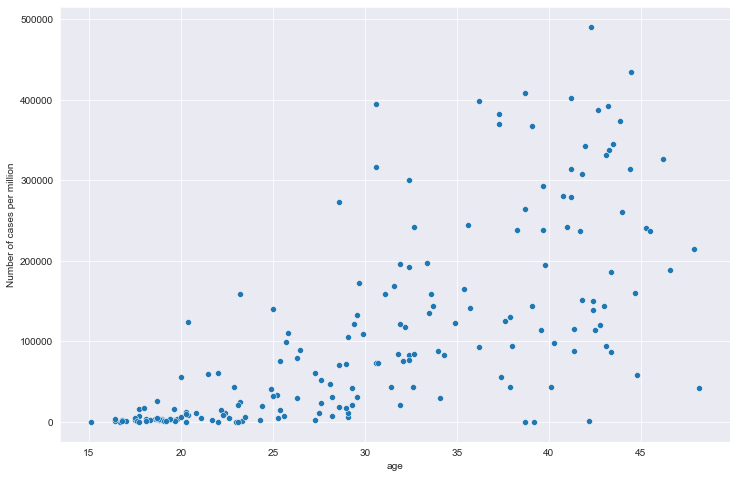
# 全部国家每百万人累计病例&年龄中位数关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_cases_with_age.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'age']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='age', y='data')
plt.xlabel('age')
plt.ylabel('Number of cases per million')
plt.show()
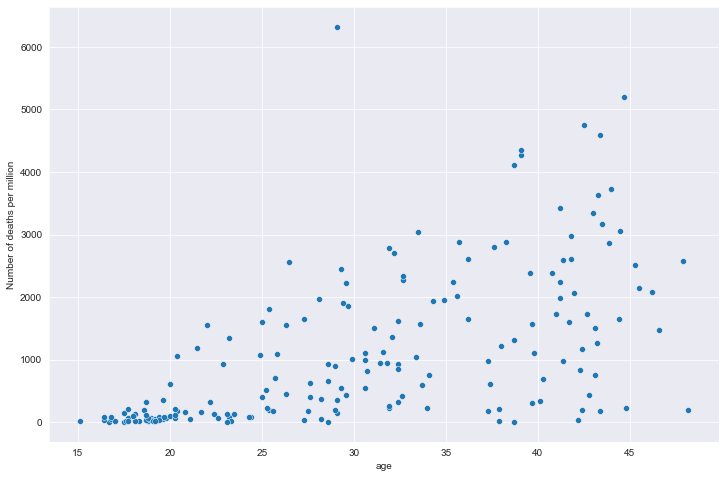
# 全部国家每百万人累计死亡&年龄中位数关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_deaths_with_age.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'age']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='age', y='data')
plt.xlabel('age')
plt.ylabel('Number of deaths per million')
plt.show()
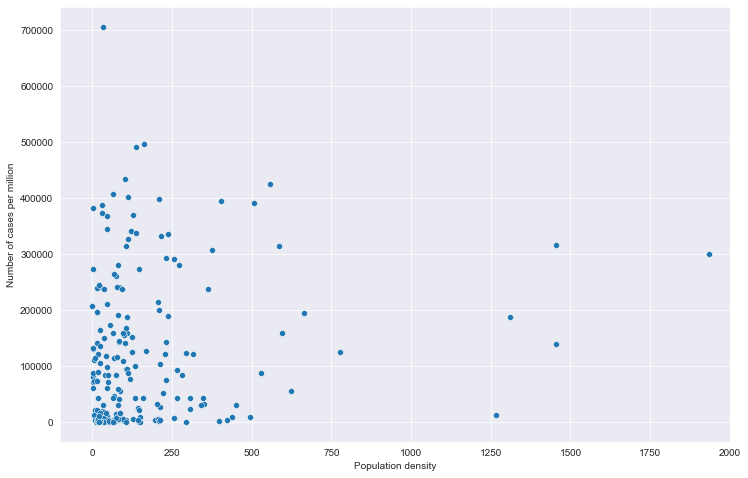
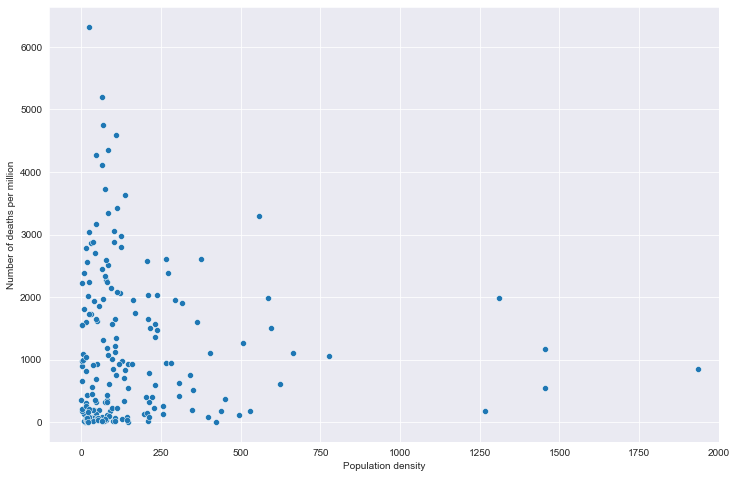
# 全部国家每百万人累计病例&人口密度关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_cases_with_density.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'den']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
fig = sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='den', y='data')
# fig.set_xticks(np.arange(0,5000,250))
fig.set_xlim(-100, 2000)
plt.xlabel('Population density')
plt.ylabel('Number of cases per million')
plt.show()
# 全部国家每百万人累计死亡&人口密度关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_deaths_with_density.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'den']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
fig = sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='den', y='data')
# fig.set_xticks(np.arange(0,5000,250))
fig.set_xlim(-100, 2000)
plt.xlabel('Population density')
plt.ylabel('Number of deaths per million')
plt.show()
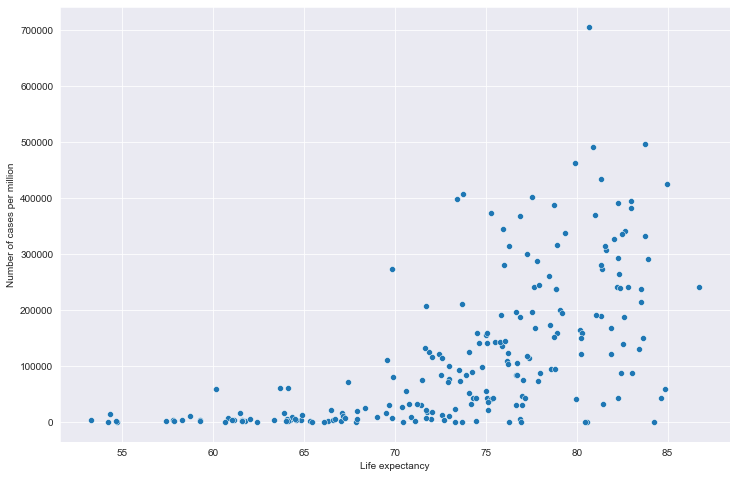
# 全部国家每百万人累计病例&期望寿命关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_cases_with_lifeexp.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'exp']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
fig = sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='exp', y='data')
plt.xlabel('Life expectancy')
plt.ylabel('Number of cases per million')
plt.show()
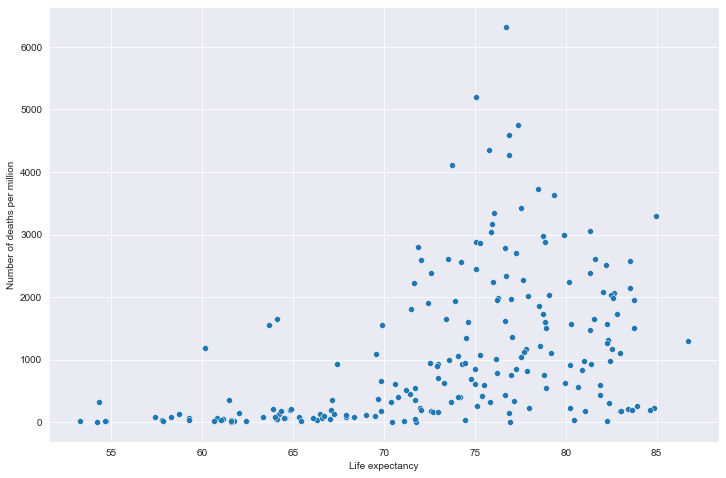
# 全部国家每百万人累计死亡&期望寿命关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_deaths_with_lifeexp.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'exp']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
fig = sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='exp', y='data')
plt.xlabel('Life expectancy')
plt.ylabel('Number of deaths per million')
plt.show()
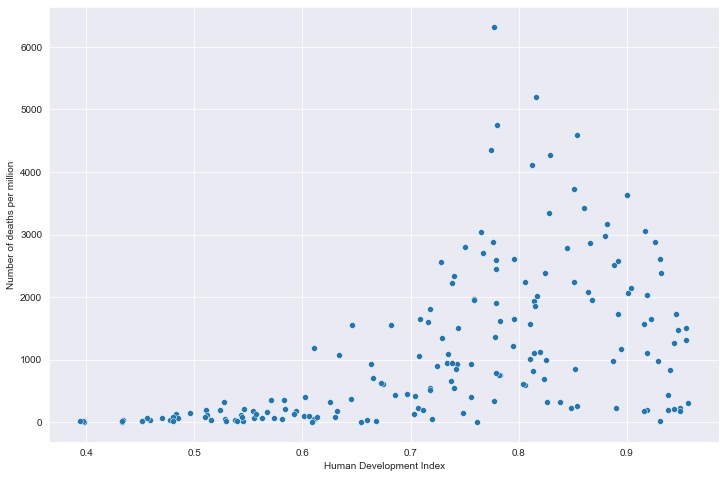
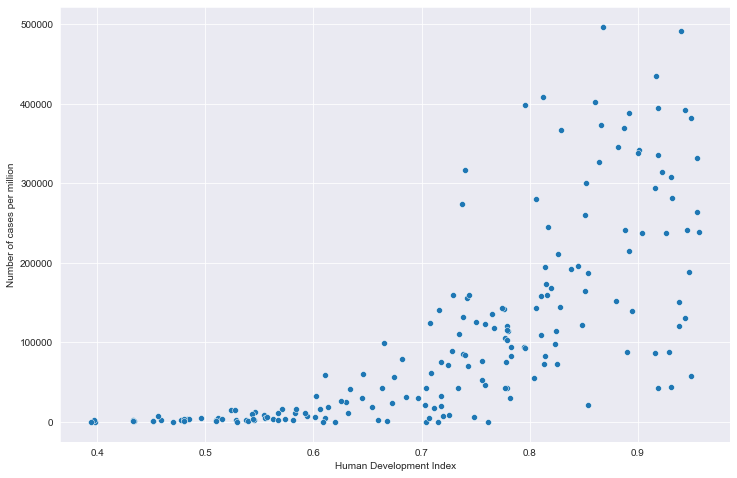
# 全部国家每百万人累计病例&hdi关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_cases_with_hdi.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'hdi']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
fig = sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='hdi', y='data')
plt.xlabel('Human Development Index')
plt.ylabel('Number of cases per million')
plt.show()
# 全部国家每百万人累计死亡&hdi关系
# 读取文件
path = "result/million_deaths_with_hdi.json"
all_data = pd.read_json(path, lines=True)
all_data.columns = ['location', 'data', 'hdi']
all_data.dropna(inplace=True)
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
fig = sns.scatterplot(data=all_data, x='hdi', y='data')
plt.xlabel('Human Development Index')
plt.ylabel('Number of deaths per million')
plt.show()
重点国家新增病例数量与疫苗剂次关系
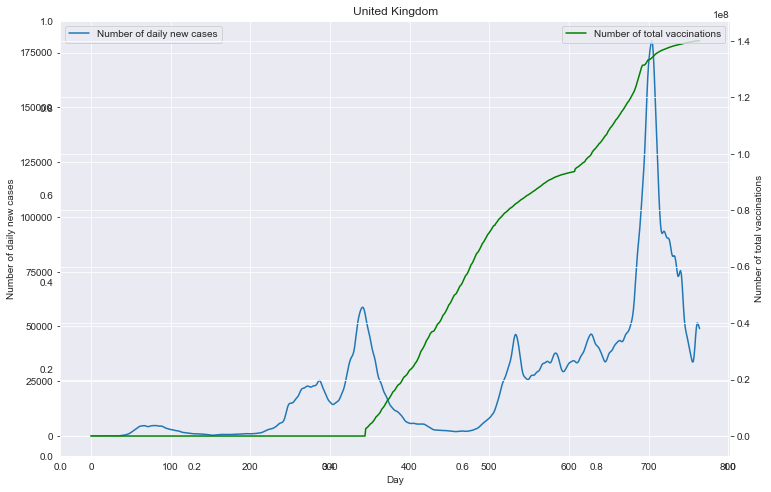
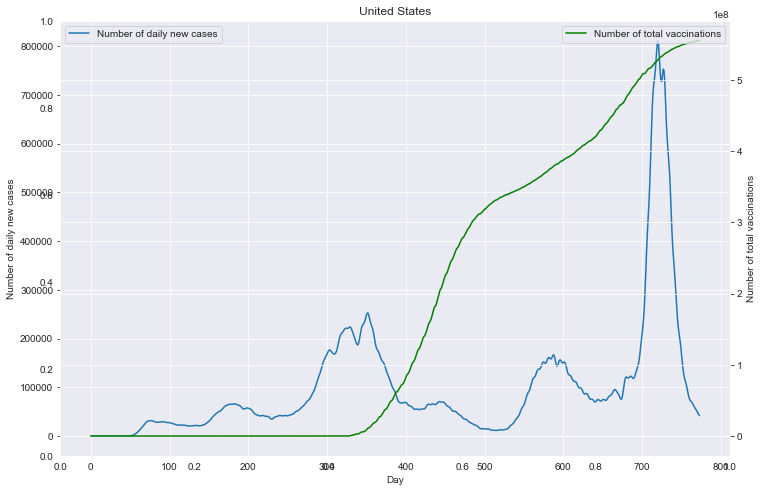
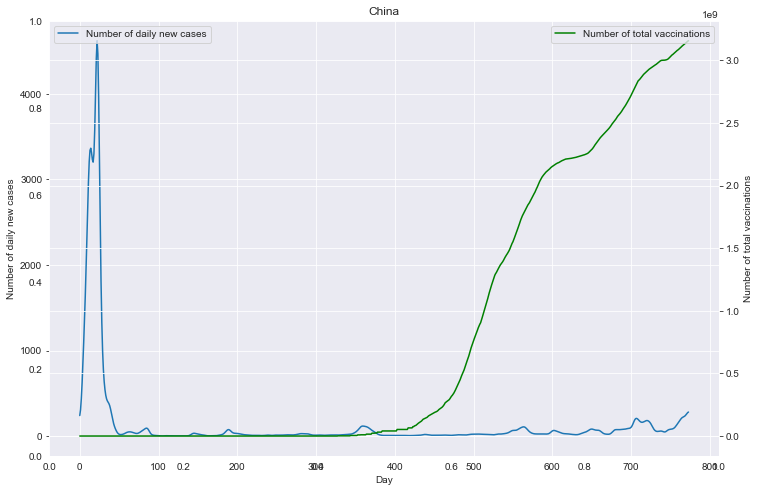
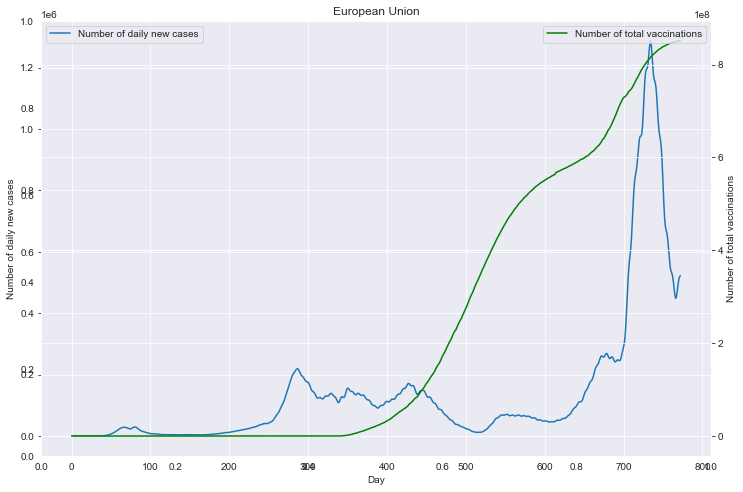

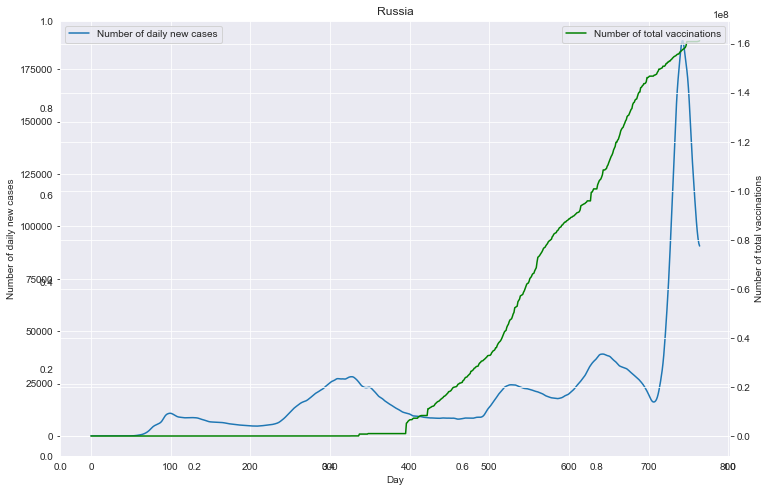
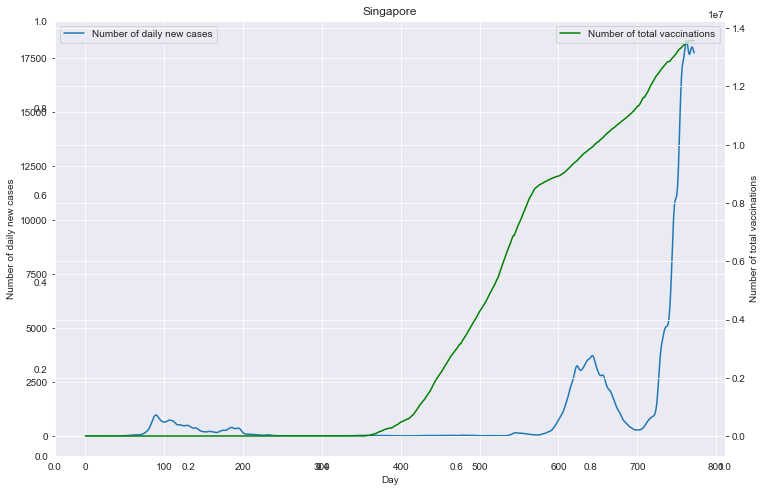
全部国家每百万人累计病例&人均GDP关系
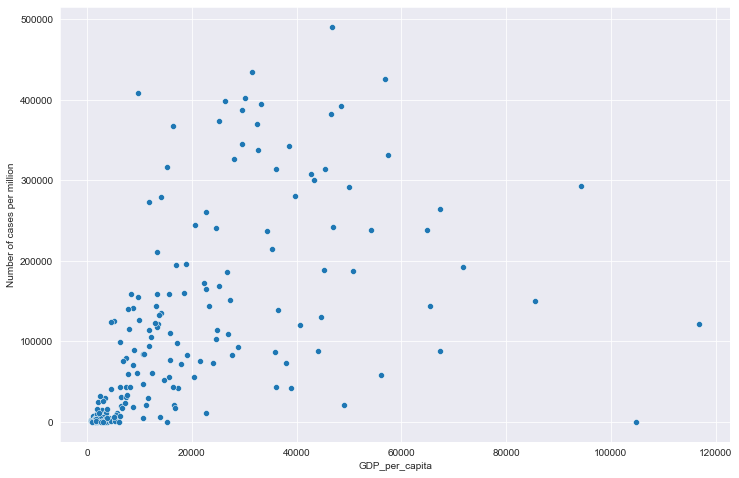
全部国家每百万人累计死亡&人均GDP关系
全部国家每百万人累计病例&年龄中位数关系
全部国家每百万人累计死亡&年龄中位数关系
全部国家每百万人累计病例&人口密度关系
全部国家每百万人累计死亡&人口密度关系
全部国家每百万人累计病例&期望寿命关系
全部国家每百万人累计死亡&期望寿命关系
全部国家每百万人累计病例&hdi关系
全部国家每百万人累计死亡&hdi关系